Beyond Widgets: Navigating the Realm of Render Objects in Flutter
A Journey Through the Building Blocks of Flutter's UI Magic
Introduction :
Welcome to a fascinating journey into the heart of Flutter's UI magic! In this blog, we are going to the world beyond widgets. This other world is the world of Render Objects.
As Flutter developers, we know how important widgets are for creating cool app designs. But have you ever wondered what's behind these widgets? Get ready to uncover the secrets of render objects, the hidden power that makes stunning visual experiences possible.
Everything is a widget in Flutter:
Everything is a widget in Flutter every flutter developer has heard this magical line in his learning experience. But do you know it is not completely true? As flutter developers, we mostly write and develop code via flutter widgets. But what if I tell you the UI that you see on the screens is not directly drawn from the widgets? Let’s see what happens.
When we want to display something on the screen we usually do it with the help of widgets. These widgets are used to create Elements in flutter and Render Objects are created from these Elements. So the flow is like this -
Widget —> Element -> Render Object
Widget :
A widget is like a blueprint that defines how a part of your app should look and behave. It can represent anything from a button or a text box to more complex things like a whole screen or even a small animation. But widgets are immutable which means once a widget is created with certain properties and configuration, it cannot be changed directly. So how does UI updation happen in Flutter ?? That’s where Elements come into the picture.
Element :
Elements in Flutter are used to keep track of what needs to be displayed on the screen and efficiently update only the parts of the UI that have changed. Think of elements as the actors that perform the roles defined by the widgets in your app's UI.
Render Object :
Render objects are the actual visual elements that appear on your device's screen. They take the information from the elements and turn it into pixels that your eyes can see. Imagine rendering objects as the artists that take the script (elements) and create the beautiful masterpiece that is your app's user interface.
Trees in Flutter :
Every Flutter developer knows that there is a widget tree in the Flutter application. But did you know there are a total of three trees in a flutter?
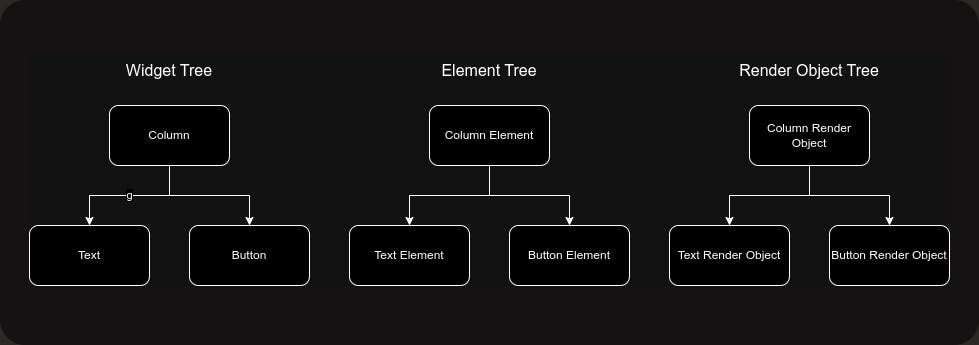
Widget Tree -
A widget tree is a hierarchical structure made up of various widgets that work together to create the user interface of your Flutter app. Just like how a family tree represents the relationships between family members, a widget tree represents the relationships between different UI elements in your app.
Element Tree -
An element tree is a dynamic representation of the current state of your app's user interface. It works in conjunction with the widget tree to efficiently manage and update the UI as it changes over time. While the widget tree describes the structure and configuration of your UI, the element tree keeps track of the actual instances of widgets that are currently being displayed on the screen.
Render object Tree -
A render object tree is a hierarchical structure that represents the visual layout and rendering of your app's user interface. While the widget tree and element tree define the structure and state of your UI, the render object tree handles the actual rendering of the visual elements on the screen.
Suppose we have a simple UI where we have text and a button inside of a column widget. Then three trees are going to be like this -
UI Updates via Element Tree :
Consider the same widget tree from above where we have a Text widget and a Button inside a Column widget. Suppose the initial value of the Text is “Music” and on click of the button text widget changes to “Dance”. So let’s see how this UI updation happens at the tree level in Flutter. So initially widget, element and render object trees are going to be like this -
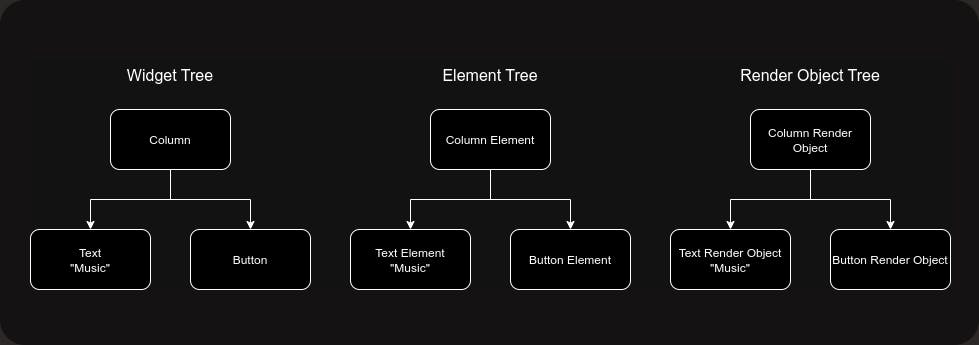
Now as explained earlier Widgets are immutable so if we change the Text widget then it will not just reassign a new one to the widget tree but it will create a new Text object with a new value i.e. “Dance” in our case.
But on the other hand, Elements are mutable. So when any changes happen to the widget tree Element tree check the following condition -
Do previous and new widgets have the same type?
Do previous and new widgets have the same key?
If both conditions are true then Element Tree just swaps the value of the previous element object with the new value. Then this updated element tree is passed to the render object tree to paint the updated UI.
So reusing the same object in element tree flutter saves a lot of memory and provides faster performance. Hot reload uses this behaviour of the element tree to update UI faster in the development of the application.
So updated trees look like this -

That concludes our tour of Flutter's widget, element, and render trees! By understanding these three pillars of Flutter's reactive framework, you now have the insider's view of how Flutter builds UIs and efficiently handles mutations. Congrats on learning about widget trees, element trees, and render trees.
Keep Fluttering 💙💙💙