Unlocking the Secrets of Clean Architecture: Building Scalable Flutter Apps : Part-1
Elevate Your Flutter Apps: Building for Scalability with Clean Architecture
Building a complex app in Flutter can be challenging, especially when it comes to managing the app's architecture. That's where Clean Architecture comes in. Clean Architecture is a software architecture pattern that separates the app's concerns into distinct layers, making it easier to maintain, test, and extend the app over time.
In the context of Flutter, Clean Architecture can help you create a robust, scalable, and maintainable mobile application. In this Blog, we will go through Flutter Clean Architecture and its concepts. This is going to be a multi-part blog series so stay tuned for that. This is the first part of the series and throughout the series, we are going to build a complete flutter application with all corner cases covered. This Flutter Architecture is highly inspired by Reso Coder so be sure to check his tutorials as well on youtube.
What are Clean Architecture Layers?
In Clean Architecture we built applications in the context of features, meaning we built application feature by feature and we use all these layers for each feature we implement. So there are majorly three layers -
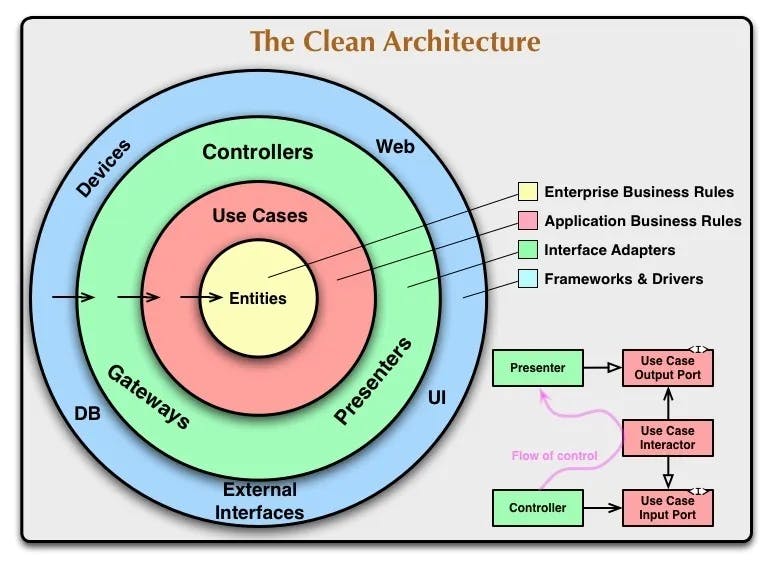
Presentation - (User Interface)
Widgets
Logic Holders (BLoC)
Domain - (Business Logic)
UseCases
Entities
Contract of Data Repositories
Data -
Repository Implementation
Remote Data Sources
The presentation Layer is the Layer we commonly know from base flutter architecture. It contains all the UI stuff of the application. It also contains any Logic holders like BLoC. This is specific to the State management Package you choose, I prefer BLoC you can use Providers or Riverpod or GetXControllers, etc. So the presentation Layer contains Pages/Screens, BLoC and Widgets.
The Domain Layer contains the business logic of the application. This layer contains Entities, UseCases and Repository Contracts. But what are those 🤔 ?
Entities are the Classes that carry the data that is displayed on the User Screen. They are like the models we used in normal flutter projects. But entities will only contain relevant information and there will be no fromJson() and toJson() methods or any kind of logic.
The UseCases represent the actions that the application can perform. For each feature, we create a UseCase.
Repository Contracts are the layer of abstraction in the UseCase and Data layer. This allows the domain layer to be independent of the Data layer. These are created using Abstract Classes in Dart.
The data Layer is the layer that interacts with the API world. This layer is responsible for getting the data from remote sources and converting them to dart objects as well. So it contains three things: Models, Repositories and Data Sources. Models are the dart classes that store the entire API response meaning it contains the JSON serialization logic. Data sources are the one who does the API call. Repositories are the ones that call the function from a data source and convert them to dart objects.
Let’s take an overview -
Here is the sequence of events that happens -
Data sources call the external API and receive the data in JSON format and forward it to the Repository of the Data Layer.
Then the repository of the Data layer converts this data into Models using Json Conversion.
Then this converted data is passed to the UseCase of the Domain Layer.
Then UseCases return the Entity to the Presentation Layer’s BLoC.
Then BLoC emits the proper state to notify the UI about the changes.
Let’s see what are we going to build in this blog series -
We are going to build a Music Application which contains just two pages. On the first page, we are going to get a list of all songs. The second page will be displaying the details and lyrics of a particular song.
Prerequisites -
Flutter Basic knowledge
Basic Knowledge of OOPS
Knowledge about BLoC
A lot of time and excitement
First, we will be importing some packages that we are going to use in the application. This is the link to the source code - Link.
Packages -
connectivity_plus: ^4.0.0
dio: ^4.0.6
equatable: ^2.0.3
flutter_bloc: ^8.0.1
fpdart: ^0.6.0
get_it: ^7.6.0
The Connectivity package is to check internet connectivity and show proper error messages when the device is not online. The Dio package is used for API calls. fpdart is a special package that we will use for handling errors. This package provides the use of Either keyword -
Either<L, R>: L is the type of the error, and R is the return type when the computation is successful. You will understand it better when we write the code of error handling, so follow along.
The get_it package is used for managing the dependencies of the application.
Now let’s take a look at the folder structure of the application.
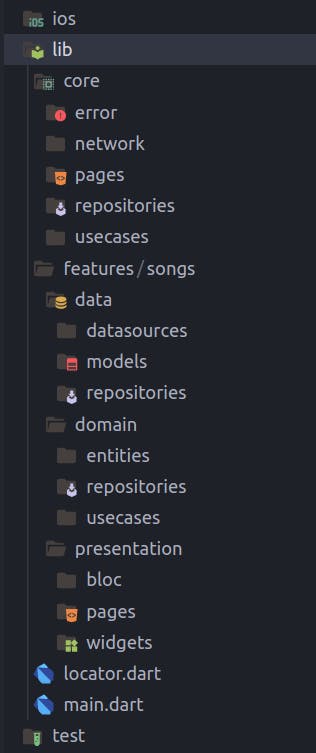
The core folder contains files that are not specific to a feature, they are being used in multiple locations in the entire application.
The features folder will contain all the features of the application in our case it's just one.
Each feature will contain Domain, Data and Presentation folders.
Domain Folder will have Entities, UseCases and Repository folders.
The data folder will contain data sources, repositories and models.
The Presentation folder will contain pages, Bloc and commonly used widgets in that feature.
So that’s it for this Blog, In this Blog we learned about what is clean architecture and why to use it. Then we learned about different layers in clean architecture and also the flow of the data.
Then we have done the first step of the application by installing the required packages and defining the project structure.
In the next blog, we will start with implementing each Layer one at a time.
So until then Happy Fluttering 🐦 🐦