GitHub Actions
Github Actions CI for Pushing Docker Image to DockerHub Registery
In this article, we are going to build a complete CI/CD pipeline that builds a docker image from our project hosted on GitHub and publish that image on the docker hub. We are going to achieve this by using a tool called GitHub Actions.
GitHub Actions is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform that allows you to automate your build, test, and deployment pipeline.
DockerHub is a platform where we host our docker image which can be publicly available just like we host our project on GitHub.
So the prerequisite to this article is to have a DockerHub account and a GitHub account.
First, we need a project from which we can build a docker image. So you can use any project. I am going to use one of my Golang projects for this article.
As the article is focused on CI/CD not on actual what a project is so I am not going into details about the project.
So if you want to follow the same project used in this article use the above link to clone the repository.
We need to have a Dockerfile for the project which can build an image of our project. I already have an article about How to write a docker file, so if you are not aware of that please check that out LINK.
So now to set up GitHub Actions on your project you just need to create a .github folder in the root directory.
GitHub will automatically recognize the .github folder and will run the config files inside them.
Create a docker-image.yml file inside the .github folder.
name: Docker Image CI
on:
push:
branches: [ "master" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "master" ]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Build the Docker image
run: docker build . --file Dockerfile --tag go-restro:latest
- name: Build and Push Docker Image
uses: mr-smithers-excellent/docker-build-push@v4
with:
image: pranav18vk/go-restro
registry: docker.io
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_PASSWORD }}
Now first let’s take a look at our config file :
name: This attribute is used to give the name to your CI or any jobs.
on: This is used to declare when we want to run this config file. So we have two rules first is push and the other is pull_request, and each of them consists of which branch it should target.
In our case, we want to build and deploy whenever we have to push into the master branch.
runs-on: This represents which base image should be used for the execution of the job.
steps: Defines the steps to be executed in a job
uses - actions/checkout@v3 is used to pull the latest code from the repository
run - executes Linux command, in our case, it is a docker build
with - Here we defined steps to push the image to the docker hub, we give parameters like image name, registry in our case it's docker and docker username and password.
NOTE: Docker username and password are stored as repository secrets.

Now we have created our config file, just commit these changes to the master branch.
Now, whenever you create a pull request or push to the main branch will trigger the pipeline.
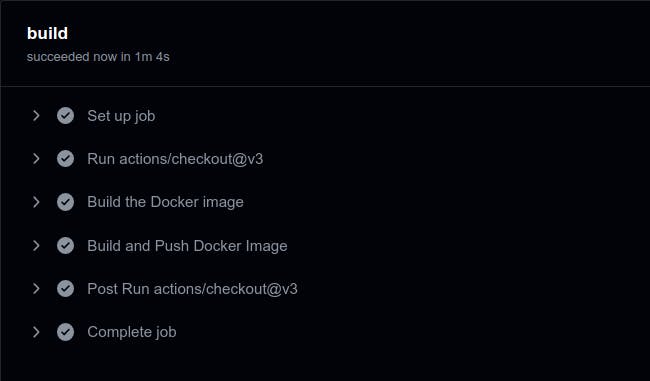
Congratulations!!! You have successfully created your first CI pipeline with GitHub Actions.
